How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that blends technical understanding with responsible practice. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from selecting the right aircraft and conducting thorough pre-flight checks to mastering basic and advanced flight maneuvers. We’ll cover everything from understanding different drone types and their unique control mechanisms to navigating safety regulations and troubleshooting common issues.
Prepare to take flight with confidence and expertise.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to operate a drone safely and responsibly. We will explore various drone types, pre-flight procedures, essential flight controls, advanced techniques, battery management, troubleshooting strategies, and crucial safety regulations. By the end, you will possess a strong foundation for operating your drone with confidence and minimizing potential risks.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the differences between quadcopters, hexacopters, octocopters, and fixed-wing drones, highlighting their control mechanisms and typical applications.
Multirotor Drone Operation: Quadcopter, Hexacopter, and Octocopter
Multirotor drones, including quadcopters (four rotors), hexacopters (six rotors), and octocopters (eight rotors), utilize multiple rotors for lift and maneuverability. The primary difference lies in redundancy and stability. Quadcopters are the most common, offering a good balance of simplicity and stability. Hexacopters and octocopters provide increased redundancy; if one or two rotors fail, the drone can still maintain controlled flight.
Control is achieved through manipulating the speed of individual rotors, tilting the drone in various directions.
Fixed-Wing Drone Operation
Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, operate differently from multirotor drones. They rely on forward motion for lift, generated by their wings. Control is achieved through ailerons (for roll), elevators (for pitch), and rudder (for yaw). They generally require a runway for takeoff and landing, and their maneuverability is more limited compared to multirotor drones. Their flight characteristics, however, allow for longer flight times and greater range.
Drone Type Comparison
| Type | Control Method | Flight Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quadcopter | Rotor speed control | Highly maneuverable, relatively short flight time | Aerial photography, videography, inspection |
| Hexacopter | Rotor speed control | Highly maneuverable, longer flight time than quadcopter, increased redundancy | Heavy payload delivery, aerial mapping |
| Octocopter | Rotor speed control | Highly maneuverable, longest flight time among multirotors, highest redundancy | Precision agriculture, search and rescue |
| Fixed-Wing | Ailerons, elevators, rudder | Longer flight time, greater range, less maneuverable | Aerial surveying, long-range surveillance |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight checks are essential for safe drone operation. This section details a checklist for inspections, emphasizes the importance of regulatory compliance, and Artikels a safe pre-flight procedure.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Battery level and condition (ensure fully charged and no visible damage)
- Propeller integrity (check for cracks or damage)
- GPS signal strength (ensure a strong and stable signal)
- Gimbal functionality (if applicable, test its movement and stability)
- Camera functionality (if applicable, test its operation and image quality)
- All other components for any damage or looseness.
Regulatory Compliance and Airspace Restrictions
Before every flight, it’s crucial to check for and comply with local regulations and airspace restrictions. This may involve registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and avoiding restricted airspace such as airports and military zones. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal consequences.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Safe Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart, How to operate a drone
A systematic approach to pre-flight procedures ensures safety. The following steps represent a typical flowchart, but always refer to your drone’s specific manual:
- Power on the drone’s remote controller.
- Power on the drone itself.
- Check for GPS signal lock.
- Perform pre-flight checks (battery, propellers, etc.).
- Verify airspace restrictions and regulations.
- Select a safe and open flight area.
- Calibrate the compass if needed.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration.
- Ready for takeoff.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. This section will cover techniques for various wind conditions, obstacle avoidance, and emergency landing procedures.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Techniques
For takeoff, gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a stable hover before proceeding with any maneuvers. Landing should be performed in a controlled manner, gradually lowering the drone until it gently touches down. In windy conditions, use caution, adjusting your control inputs to compensate for wind gusts. Consider landing in a sheltered area if wind conditions are severe.
Obstacle Avoidance
Before takeoff, carefully assess the area for potential obstacles, including trees, buildings, and power lines. Maintain a safe distance from obstacles during flight, using the drone’s camera and sensors (if equipped) to aid in navigation. Always prioritize safety over achieving a specific shot or maneuver.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of system failure (e.g., low battery, GPS loss, motor malfunction), immediately initiate an emergency landing procedure. This usually involves prioritizing a safe landing location, gently lowering the drone to the ground while maintaining control as much as possible. If complete control is lost, the drone’s emergency stop function (if available) should be activated.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section explains the functions of control sticks and details how to perform basic maneuvers.
Control Stick Functions
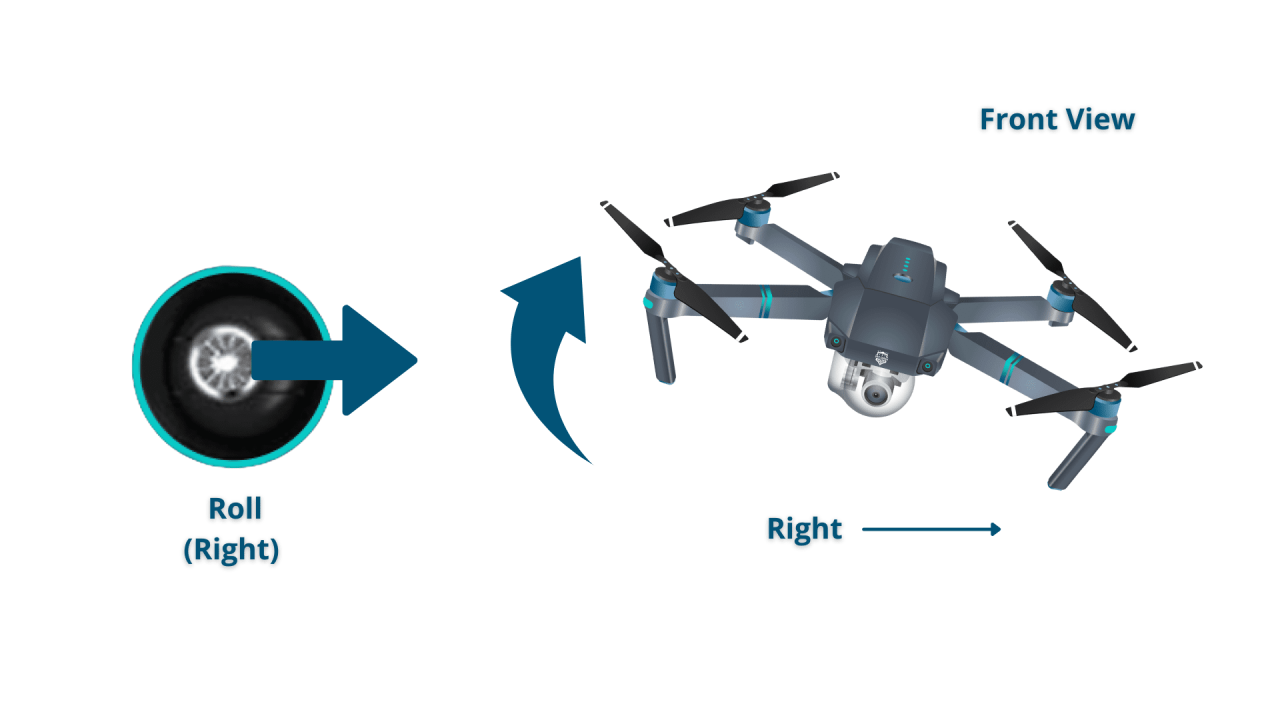
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks (or thumbsticks). One typically controls the drone’s altitude and forward/backward movement, while the other controls its left/right movement and rotation (yaw). Precise control is essential for smooth and stable flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Hovering involves maintaining a stable position in the air. Ascending and descending control the drone’s altitude. Yawing refers to rotating the drone around its vertical axis. Mastering these basic maneuvers is essential before attempting more complex flights.
Executing a Smooth 360-Degree Turn
To execute a smooth 360-degree turn, gently push the yaw stick in one direction while maintaining a stable altitude and position. The rate of rotation can be adjusted by the speed and smoothness of your joystick input. Practice this maneuver in an open area to develop a feel for the drone’s responsiveness.
Advanced Flight Techniques
This section explores challenging flight scenarios, including flying in windy conditions and using GPS waypoints for automated flights, along with safety considerations for aerial photography and videography.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires skill and caution. Strong winds can affect the drone’s stability and control, making it more challenging to maintain a stable hover or perform precise maneuvers. Practice flying in light winds to develop the skills necessary for handling stronger winds. Avoid flying in extremely windy conditions.
Using GPS Waypoints
Many drones allow for the creation of flight plans using GPS waypoints. This enables automated flights, allowing the drone to follow a pre-defined path. Proper planning and configuration are crucial for safe and successful waypoint flights. Always review the planned flight path before initiating the automated sequence.
Safety Considerations for Aerial Photography and Videography
Aerial photography and videography demand additional safety precautions. Always maintain awareness of your surroundings, ensuring that the drone remains a safe distance from people and obstacles. Be mindful of privacy concerns and avoid capturing images or videos without permission.
Drone Battery Management and Care

Proper battery management is crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone batteries and ensuring safe operation. This section provides best practices for charging, storing, and monitoring battery levels.
Charging and Storing Drone Batteries
Always use the recommended charger for your drone’s batteries. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, as this can damage them. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Proper storage helps maintain battery health and longevity.
Monitoring Battery Levels
Closely monitor battery levels during flight, paying attention to low-battery warnings. Plan your flights to allow for sufficient time to return to your starting point before the battery depletes completely. A sudden power loss mid-flight can lead to a crash.
Common Battery-Related Issues and Troubleshooting
Common battery problems include swelling, reduced capacity, and failure to charge. Troubleshooting steps may involve checking the charger, inspecting the battery for damage, and trying a different battery. If problems persist, contact the manufacturer for support.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems: How To Operate A Drone
This section identifies common drone malfunctions and provides troubleshooting steps and preventative measures.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the fundamentals, and a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you’ll be ready to explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography with your drone.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common issues include GPS signal loss (check for obstructions, ensure sufficient satellites are acquired), motor failures (inspect motors and wiring for damage), and low battery warnings (monitor battery levels, land immediately if necessary).
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, weak signal | Relocate to an open area, recalibrate GPS | Fly in open areas, maintain sufficient satellite lock |
| Motor Failure | Motor damage, wiring issues | Inspect and repair or replace damaged components | Regular inspections, avoid crashes |
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge | Land immediately, recharge battery | Monitor battery levels, plan flights accordingly |
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Understanding and adhering to drone regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible and safe drone operation. This section highlights key safety considerations.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions

Regulations vary by country and region. It is essential to research and understand the specific regulations applicable to your area before operating a drone. This includes registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and limitations on flight altitudes and distances.
Maintaining Safe Distance
Always maintain a safe distance from people, buildings, and other obstacles during flight. Avoid flying over crowds or sensitive areas. Responsible operation minimizes the risk of accidents or damage.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves understanding your drone’s capabilities and limitations, adhering to regulations, and prioritizing safety. This includes regularly inspecting your drone for damage, practicing safe flight techniques, and being aware of your surroundings.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation in understanding the various aspects of safe and effective drone piloting. Remember, consistent practice, adherence to safety regulations, and continuous learning are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone operator. Soar responsibly and enjoy the exciting world of aerial exploration!
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models known for their ease of use and positive user reviews.
How far can a drone fly?
The maximum flight distance varies significantly depending on the drone model, battery life, and environmental conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for its stated range, keeping in mind that this can be reduced by factors like wind and signal interference.
What are the legal restrictions on drone flying?
Drone regulations vary by country and region. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific rules regarding airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and permitted flight zones before flying.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements depend on your location and the drone’s specifications. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific guidelines and procedures on registering your drone.
